Market Mantra – December 2014.
– Vishal Dhawan, Chief Financial Planner, Plan Ahead Wealth Advisors.
The year 2014 was mostly a year full of positive events for Indian financial markets which caused the equity markets (BSE Sensex) gaining close to 30% in 2014 . Some of the major events that took place are as follows and our outlook in 2015:
1. Historical electoral results – A strong, pro- growth oriented and business friendly government looks good for economic growth and for businesses. This promise has to translate into big reforms on the ground as most of the early work has been focused on getting the bureaucracy and decisions that were deferred forward.
2. The GDP growth for Q3 2014 expanded to 5.3% from 5.7% in Q2. It is expected to pick up further to 6-6.5% YOY in FY16 with growth over other parts of the world remaining subdued and hence the gap of India GDP Growth with Global GDP growth is expected to widen as seen from the data below:
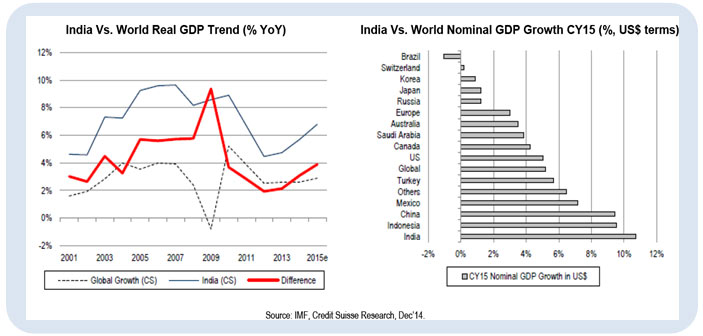
Source: IMF, credit Suisse Research, Dec 2014
3. Current Account Deficit (CAD) widened in 2Q FY15 due to widening of trade deficit. However, it is expected to be in a comfort zone in FY16 with falling crude oil prices offsetting high import growth of non-oil and gold.
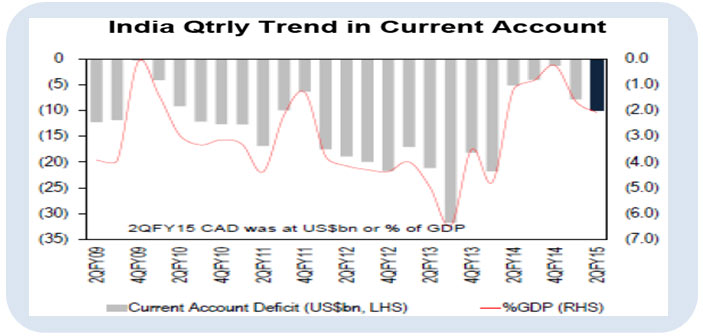
Source: RBI, Citi Research, Dec’14
4. Fiscal Deficit for the first 8 months of FY15 (Apr-Nov) came in at 99% of the budget estimate of 4.1% for the full fiscal year. Whilst it is still possible that the government could achieve the target by controlling spending for this year, the fiscal deficit target of 3.6% of GDP in FY16 could be difficult to meet.
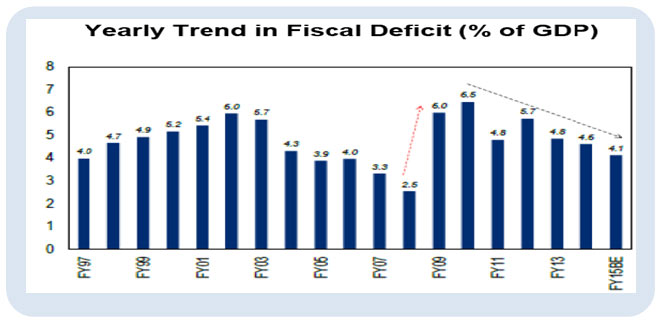
Source: Budget Documents, Citi Research, Nov’14, BE=Budgeted Estimate
5. Earnings Growth: The private sector in India remains in a deleveraging cycle, saddled with excess debt. However, Corporate Earnings should be better than estimates as corporate margins are significantly below the long term averages and should improve gradually as capacity utilization and business conditions improve in the next 2-3 years which is when the full impact of lower interest costs and softer commodity prices will show up in corporate profits.
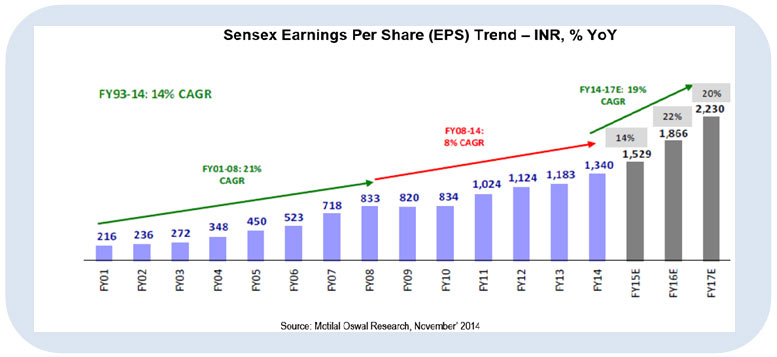
Source: Motilal Oswal Research, November 2014
The outlook for equities in 2015 could be challenging, but things look promising from a longer term perspective and there is merit in increasing allocation to equities in a phased manner and staying invested. However, every investor should look at their own specific asset allocations rather than specific asset class performances.
6. Inflation declined to a series low due to lower commodity prices, slowdown in consumer demand, low growth in MSPs and falling oil prices. CPI inflation eased to a series-low 4.4% in November 2014 from 5.5% in October 2014 in year-on-year (y-o-y) terms. This primarily reflected a sharp decline in food inflation to 3.6% in November 2014 from 5.7% in October 2014, as well as a fall in core-CPI to 5.5% from 5.9%. In fact, WPI inflation declined to 0% in November 2014.
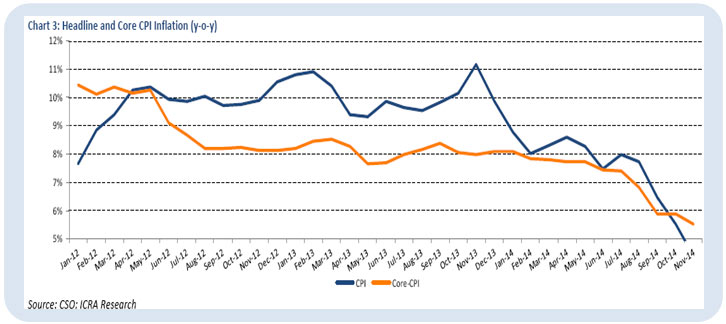
Source: CSO, ICRA Research
In the December Policy review, RBI kept the rates unchanged and revised the CPI target to 6% for March 2015 and also as per RBI, the risks to the Jan 2016 CPI target of 6% looks balanced. There could be concerns during the first quarter of 2015 as RBI waits for certainty with regards to lower/stable inflation, and fiscal adjustments during the budget before commencing any monetary easing and interest rate cuts. Global concerns over interest rate hike in US and movement of global crude oil prices will also keep investors guessing on the direction of interest rates in India.
Fall in inflation and slow economic growth would lead to cut in interest rates in future. As seen from the chart below, bond yields have moved sooner than policy rates more often. Currently also, the yields have fallen in anticipation of a rate cut.
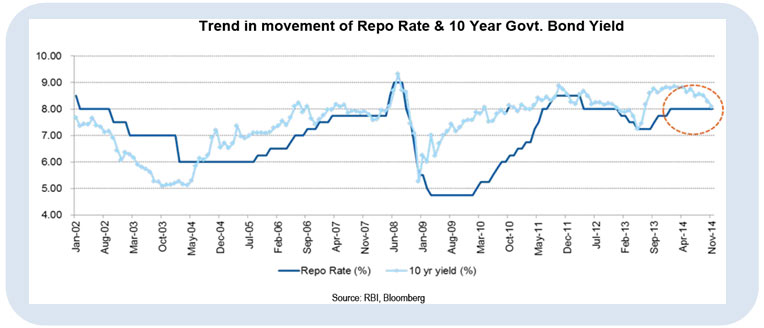
Source: RBI, Bloomberg
RBI is also targeting a real positive return on interest rates to potentially move savings from physical assets to financial assets. This could mean that a 6% CPI inflation would synchronize with a 7% repo rate – which means a 100 bps cut in repo rate over the next 18 months.
Investors will need to have a sufficiently long time horizon ( 12-24 months) when investing in duration strategies now, especially given that the first 25 bps of the expected cuts are perhaps already in the price. Thus, we would recommend continuing to stay invested in a portfolio with a mix of longer maturities and accrual funds, which are likely to benefit as interest rates are expected come down in the next 18-24 months.
7. The global equity markets also continue to perform well with US markets reaching new highs. Crude oil prices corrected to a 5.5 year low due to significant new supply of shale gas from U.S., slowdown in global demand, and a reduction in per unit consumption in automobiles due to better and efficient technology. So, there’s enough reason to believe that oil prices will remain favourably low. Obviously, a sharp drop in oil prices can potentially create some pressures in oil exporting countries like Russia and in market players who were perhaps overextended in trading.
Also, lower oil prices reduce inflationary pressures and current account deficits allowing emerging market central banks greater freedom to stimulate domestic economies.
We think 2015 is going to be a year of divergence in economic growth and central bank policy. While the US is leading developed markets growth, Europe and Japan are struggling for growth at this point of time and China is still in search of its sustainable growth formula. So we could have central banks across the globe moving in a de-synchronized manner where US is looking to normalize its interest rate structure, while Japan and Europe will still continue to adopt loose monetary policy conditions to fight deflation in their economy. This divergence in policy action will increase market volatility and require investors to pay more attention to risk management.
8. Currency: Dollar strength and one of the drivers of this trend is the shale gas revolution which US is experiencing and its impact on shrinking the US economy’s current account deficit. This could pose some challenges for emerging markets but stronger fundamentals should limit the financial risks for those emerging market which have already gone through a course correction over the last 18 to 24 months.
Hence, we continue to reiterate to build a well diversified portfolio with having exposure of between 10-15% into international investments to hedge against currency risk.
9. Gold prices could continue to remain under pressure in the short term due to the fear of interest rate hike in US. Whilst the INR currently looks a little overvalued and is expected to depreciate, Gold as an asset class could gain value as it has an inverse relationship with the Indian currency traditionally.
Hence, we continue to believe to have gold as small part of the portfolio for the purpose of diversification and hedge currency risk.
